In today’s digital world, cloud storage has become a game-changer for individuals and businesses alike. It offers unmatched flexibility, security, and accessibility, making data management easier than ever before.
What Is Cloud Storage and How Does It Work?

Cloud storage is a technology that allows users to store data on remote servers accessed via the internet. Instead of saving files on a local hard drive or physical device, data is uploaded to data centers managed by cloud service providers. These centers are equipped with advanced infrastructure to ensure high availability, redundancy, and security.
Understanding the Core Mechanism
When you upload a file to the cloud, it’s broken into smaller chunks, encrypted, and distributed across multiple servers. This process, known as data replication, ensures that even if one server fails, your data remains safe and accessible. The cloud provider manages the backend infrastructure, including servers, networking, and storage devices, so users don’t need to worry about maintenance.
- Data is stored in geographically distributed data centers for redundancy.
- Encryption is applied both in transit and at rest to protect sensitive information.
- Users access their files through web portals, desktop apps, or mobile applications.
Types of Cloud Storage Models
There are three primary models of cloud storage: public, private, and hybrid. Public cloud storage, offered by companies like Google and Amazon, is shared among multiple users and is cost-effective. Private cloud storage is dedicated to a single organization, offering greater control and security. Hybrid cloud combines both, allowing businesses to store sensitive data on-premises while using public clouds for less critical information.
“The cloud is not about replacing your IT infrastructure; it’s about enhancing it.” — Satya Nadella, CEO of Microsoft
Top 7 Benefits of Cloud Storage
Cloud storage offers a wide range of advantages that make it an essential tool in modern computing. From cost savings to improved collaboration, the benefits are both practical and strategic.
1. Cost Efficiency and Scalability
One of the most compelling reasons to adopt cloud storage is its cost-effectiveness. Traditional data storage requires significant investment in hardware, maintenance, and IT staff. With cloud storage, you pay only for what you use, often on a subscription basis. This pay-as-you-go model allows businesses to scale up or down based on demand without upfront capital expenditure.
For example, a startup can begin with a few gigabytes of storage and expand as it grows, avoiding the need to purchase expensive servers. According to a report by Gartner, organizations that migrate to the cloud can reduce IT infrastructure costs by up to 30%.
2. Enhanced Data Security and Compliance
Contrary to common misconceptions, cloud storage often provides better security than on-premises solutions. Leading providers invest heavily in cybersecurity, employing advanced encryption, multi-factor authentication, and continuous monitoring. They also comply with international standards such as GDPR, HIPAA, and ISO 27001.
For instance, Amazon Web Services (AWS) uses end-to-end encryption and offers tools for identity and access management. This ensures that only authorized users can access sensitive data, reducing the risk of breaches.
3. Accessibility and Remote Collaboration
Cloud storage enables users to access files from anywhere with an internet connection. This is especially valuable in today’s remote work environment. Employees can collaborate in real time, edit documents simultaneously, and share files instantly—regardless of their physical location.
Platforms like Google Drive and Microsoft OneDrive integrate seamlessly with productivity tools, allowing teams to work together efficiently. A study by Microsoft WorkLab found that cloud-based collaboration tools can increase team productivity by up to 40%.
4. Automatic Backups and Disaster Recovery
Data loss due to hardware failure, cyberattacks, or natural disasters can be devastating. Cloud storage automatically backs up data, ensuring that it can be restored quickly in case of an incident. Most providers offer versioning, which allows users to revert to previous versions of a file.
For example, Dropbox maintains file history for up to 180 days on its Professional plan, enabling users to recover accidentally deleted or corrupted files. This feature is crucial for business continuity and regulatory compliance.
5. Environmental Sustainability
Cloud storage contributes to environmental sustainability by reducing the need for physical servers and data centers. Large providers optimize energy efficiency through advanced cooling systems, renewable energy sources, and server virtualization.
According to a report by the International Energy Agency (IEA), cloud computing can reduce energy consumption by up to 30% compared to traditional data centers. This makes cloud storage not only cost-effective but also eco-friendly.
6. Seamless Integration with Other Tools
Modern cloud storage platforms integrate effortlessly with third-party applications such as CRM systems, project management tools, and AI-powered analytics. This interoperability enhances workflow automation and data utilization.
For example, Box integrates with Salesforce, Slack, and Adobe Sign, allowing businesses to streamline document workflows. These integrations eliminate the need for manual data transfer, reducing errors and saving time.
7. Improved Performance and Uptime
Cloud providers guarantee high uptime—often 99.9% or higher—through redundant systems and global server networks. This ensures that data is always available when needed.
Google Cloud, for instance, offers a Service Level Agreement (SLA) of 99.9% uptime for its Cloud Storage service. This reliability is critical for businesses that depend on constant access to data for operations and customer service.
Popular Cloud Storage Providers in 2024
The market for cloud storage is highly competitive, with several major players offering diverse features and pricing models. Choosing the right provider depends on your specific needs, such as storage capacity, security requirements, and integration capabilities.
Google Drive
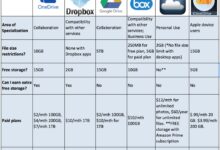
Google Drive is one of the most widely used cloud storage services, especially among individuals and small businesses. It offers 15 GB of free storage shared across Gmail, Google Photos, and Drive. Paid plans start at $1.99/month for 100 GB.
Its deep integration with Google Workspace (formerly G Suite) makes it ideal for collaborative work. Features like real-time editing, commenting, and sharing permissions enhance team productivity.
Microsoft OneDrive
OneDrive is tightly integrated with Windows and Microsoft 365, making it a natural choice for enterprise users. It offers 5 GB of free storage, with paid plans starting at $6.99/month for 100 GB and 1 TB of OneDrive storage included in Microsoft 365 Personal.
OneDrive excels in file syncing across devices and offers advanced security features like Personal Vault, which requires biometric or two-factor authentication to access sensitive files.
Dropbox
Dropbox was one of the first cloud storage platforms and remains popular for its user-friendly interface and robust sharing features. It offers 2 GB of free storage, with paid plans starting at $9.99/month for 2 TB.
Dropbox Business provides advanced admin controls, team folders, and integration with over 1,000 apps. Its Smart Sync feature allows users to access files without taking up local disk space, improving performance on devices with limited storage.
Amazon S3
Amazon Simple Storage Service (S3) is a scalable object storage service designed for developers and enterprises. It’s highly reliable, with 99.999999999% durability, and supports a wide range of use cases, from backup and archiving to big data analytics.
Pricing is based on usage, with no upfront costs. While it lacks a user-friendly interface for casual users, its API-driven model makes it ideal for custom applications and large-scale data storage.
Cloud Storage vs. Traditional Storage: A Comparative Analysis
Understanding the differences between cloud storage and traditional storage methods is crucial for making informed decisions about data management.
Cost Structure and Maintenance
Traditional storage relies on physical hardware such as hard drives, NAS (Network Attached Storage), and on-premises servers. These require upfront capital investment, ongoing maintenance, and periodic upgrades. In contrast, cloud storage operates on an operational expenditure (OpEx) model, where costs are predictable and scalable.
Additionally, cloud providers handle maintenance, software updates, and hardware replacements, freeing IT teams to focus on strategic initiatives rather than routine upkeep.
Data Accessibility and Mobility
With traditional storage, accessing files outside the office network can be challenging and often requires complex VPN setups. Cloud storage, on the other hand, is inherently mobile-friendly. Users can access their data from smartphones, tablets, and laptops with an internet connection.
This mobility supports flexible work arrangements and improves responsiveness, especially in fast-paced business environments.
Security and Data Control
While some organizations prefer traditional storage for perceived control over data, cloud providers often offer superior security measures. They employ dedicated security teams, conduct regular audits, and use advanced threat detection systems.
However, data sovereignty and compliance remain concerns for some industries. In such cases, private or hybrid cloud solutions may be more appropriate, offering a balance between control and scalability.
Security Concerns and Best Practices in Cloud Storage
Despite its many advantages, cloud storage is not without risks. Data breaches, account hijacking, and insider threats are potential vulnerabilities that users must address.
Common Security Risks
One of the most common risks is weak authentication. Using simple passwords or failing to enable two-factor authentication (2FA) makes accounts vulnerable to brute-force attacks. Another risk is data leakage through misconfigured sharing settings—accidentally making files public can expose sensitive information.
Additionally, third-party app integrations can introduce security gaps if not properly vetted. For example, a malicious app with access to your cloud storage could exfiltrate data without your knowledge.
Best Practices for Securing Your Data
To mitigate these risks, users should adopt the following best practices:
- Enable two-factor authentication (2FA) on all cloud accounts.
- Use strong, unique passwords and consider a password manager.
- Regularly review sharing permissions and revoke access for inactive users.
- Encrypt sensitive files before uploading them to the cloud.
- Monitor account activity logs for suspicious behavior.
Organizations should also implement data loss prevention (DLP) policies and conduct regular security training for employees.
How to Choose the Right Cloud Storage Solution
Selecting the best cloud storage provider requires careful evaluation of several factors, including storage needs, budget, security requirements, and integration capabilities.
Assess Your Storage and Usage Needs
Start by estimating how much data you need to store and how frequently it will be accessed. For personal use, a few hundred gigabytes may suffice. For businesses, especially those dealing with large media files or databases, terabytes of storage may be necessary.
Also consider whether you need real-time collaboration, version control, or automated backups—features that vary between providers.
Evaluate Security and Compliance Features
If you handle sensitive data—such as financial records, health information, or intellectual property—ensure the provider complies with relevant regulations. Look for certifications like SOC 2, HIPAA, or GDPR compliance.
Also check if the provider offers encryption, audit logs, and granular access controls. For high-security environments, consider zero-knowledge encryption, where even the provider cannot access your data.
Compare Pricing and Scalability
Pricing models vary widely. Some providers charge per user, others per storage volume. Be aware of hidden costs, such as fees for data transfer, API calls, or premium support.
Choose a provider that allows easy scaling without long-term contracts. This flexibility is essential for growing businesses that need to adapt quickly to changing demands.
Future Trends in Cloud Storage Technology
The cloud storage landscape is evolving rapidly, driven by advancements in artificial intelligence, edge computing, and quantum encryption.
AI-Powered Data Management
Artificial intelligence is being used to optimize storage efficiency, predict usage patterns, and automate data classification. For example, AI can identify and archive inactive files, reducing storage costs. It can also detect anomalies in access patterns, helping prevent data breaches.
Google’s AI-driven storage tiering automatically moves infrequently accessed data to lower-cost storage classes, saving users money without sacrificing performance.
Edge Computing and Decentralized Storage
Edge computing brings data processing closer to the source, reducing latency and bandwidth usage. In the context of cloud storage, this means storing data on local devices or edge servers before syncing to the cloud.
Decentralized storage networks, such as IPFS (InterPlanetary File System) and Filecoin, are also gaining traction. These use blockchain technology to distribute data across a peer-to-peer network, enhancing security and reducing reliance on centralized providers.
Quantum-Resistant Encryption
As quantum computing advances, traditional encryption methods may become vulnerable. Cloud providers are already researching quantum-resistant algorithms to future-proof data security.
For example, AWS and Microsoft are experimenting with post-quantum cryptography to ensure long-term data protection. This proactive approach will be critical in maintaining trust in cloud storage systems.
Real-World Applications of Cloud Storage
Cloud storage is not just for backing up photos or documents—it plays a vital role in various industries and use cases.
Healthcare and Electronic Medical Records
Hospitals and clinics use cloud storage to securely store and share electronic medical records (EMRs). This improves patient care by enabling quick access to medical histories, lab results, and imaging files across different facilities.
Providers like Microsoft Azure offer HIPAA-compliant cloud solutions tailored for healthcare organizations.
Education and E-Learning Platforms
Schools and universities use cloud storage to host course materials, student assignments, and video lectures. Platforms like Google Classroom and Canvas rely on cloud infrastructure to deliver content to students worldwide.
During the pandemic, cloud storage enabled seamless transition to remote learning, ensuring continuity of education despite school closures.
Media and Entertainment Industry
Streaming services like Netflix and Spotify use cloud storage to manage vast libraries of audio and video content. Cloud-based editing tools allow filmmakers and musicians to collaborate remotely, sharing large project files without physical media.
Adobe Creative Cloud, for instance, stores user projects in the cloud, enabling access from any device and automatic syncing across workstations.
What is cloud storage?
Cloud storage is a service that allows users to store and access data over the internet on remote servers managed by third-party providers. It eliminates the need for physical storage devices and enables data access from any location with an internet connection.
Is cloud storage safe?
Yes, cloud storage is generally safe, especially when using reputable providers like Google, Microsoft, or Amazon. These companies employ advanced encryption, regular security audits, and compliance with international standards to protect user data.
How much does cloud storage cost?
Costs vary by provider and plan. Many services offer free tiers (e.g., 5–15 GB), while paid plans range from $1.99 to $9.99 per month for personal use. Business plans can cost more based on storage volume, number of users, and additional features.
Can I access my cloud storage offline?
Yes, many cloud storage services allow offline access by syncing files to your device. For example, Google Drive and OneDrive let you mark files for offline use, so you can view or edit them without an internet connection.
What happens if the cloud provider goes out of business?
Reputable providers have data portability and exit strategies in place. Users are typically given ample notice and tools to download or migrate their data to another service. However, it’s wise to maintain local backups as a precaution.
Cloud storage has revolutionized the way we store, access, and manage data. From cost savings and enhanced security to global accessibility and seamless collaboration, its benefits are undeniable. As technology continues to evolve, cloud storage will play an even greater role in shaping the future of digital infrastructure. Whether you’re an individual user or a large enterprise, adopting cloud storage is no longer optional—it’s essential for staying competitive and efficient in the modern world.
Further Reading: